Strategy is the “direction and scope ” of a company (or an organization) over the long term, which allows it to achieve a competitive advantage. It is implemented by utilizing its resources and capabilities, and in order to meet the needs of the market and the fulfillment of the expectations of the stakeholders , in the context of a dynamically changing environment. (Johnson and Scholes 1999, :https://bit.ly/2VRa2aX).
Strategic management according to M. Porter (1991: https://bit.ly/2Yo6gaP),refers to the choices of products to be produced and services to be offered. Functional efficiency in their production is a prerequisite for creating a competitive advantage and value.
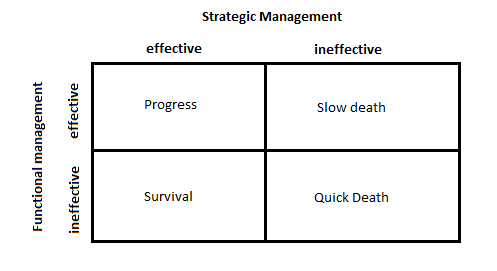
Strategy is the means of adapting the business to its environment, the frequent and unexpected changes of which are a source of risk and opportunity for profit. The best way for a business to anticipate the future is to “systematically prepare for it.” The current strategy is the result of the effects of the industry and specifically of competitors, customers and suppliers, but also of the goals, but the latter is missing, we simply have the survival of the business. In case we do not have an effective strategy (either at the time of arrest or execution) death is the result. The existence of functional efficiency or not, simply delays or aggravates death respectively, according to M. Porter, as shown in the following diagram:
 The creation of a competitive comparative advantage is a form of dynamic response of the company, aiming to cover the revenue gap that is necessary to ensure and deepen its viability. This is often achieved in a highly competitive, sufficiently unstable, fluid and unpredictable environment of intangible change, often characterized by the entropy phenomenon. In the context of a relentless, relentless, relentless and relentless competition that haunts the market and that is inevitably instilled by the unhindered action of its “five” forces, the strategy shields and secures the future of the business unscathed.
The creation of a competitive comparative advantage is a form of dynamic response of the company, aiming to cover the revenue gap that is necessary to ensure and deepen its viability. This is often achieved in a highly competitive, sufficiently unstable, fluid and unpredictable environment of intangible change, often characterized by the entropy phenomenon. In the context of a relentless, relentless, relentless and relentless competition that haunts the market and that is inevitably instilled by the unhindered action of its “five” forces, the strategy shields and secures the future of the business unscathed.